Healthy Nutrition Plan: Ultimate Guide to Balanced Eating
Creating a healthy nutrition plan is one of the most important steps you can take toward improving your health and well-being. A well-balanced diet provides the nutrients your body needs to function effectively, reduces the risk of chronic diseases, and supports overall mental and physical health. This article will guide you through the process of building a healthy diet plan, with detailed explanations divided into easy-to-read categories.
Key Components of a Healthy Nutrition Plan
1. Understanding Macronutrients
- Carbohydrates: The body’s primary energy source. Focus on complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables. They provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber, which aids digestion.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle repair and growth. Incorporate lean proteins like chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and legumes into your meals.
- Fats: Necessary for hormone production and nutrient absorption. Prioritize healthy fats such as those found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
2. Incorporating Micronutrients
- Vitamins: Vital for various bodily functions, including immune support and energy production. Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet to ensure you receive an adequate supply of vitamins A, C, D, E, and K.
- Minerals: Important for bone health, nerve function, and fluid balance. Foods rich in calcium, potassium, magnesium, and iron should be regularly included in your diet.
3. Importance of Hydration
- Water: Essential for every bodily function, including digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day.
- Other Fluids: Herbal teas, infused waters, and broths can contribute to your daily hydration needs and provide additional nutrients.
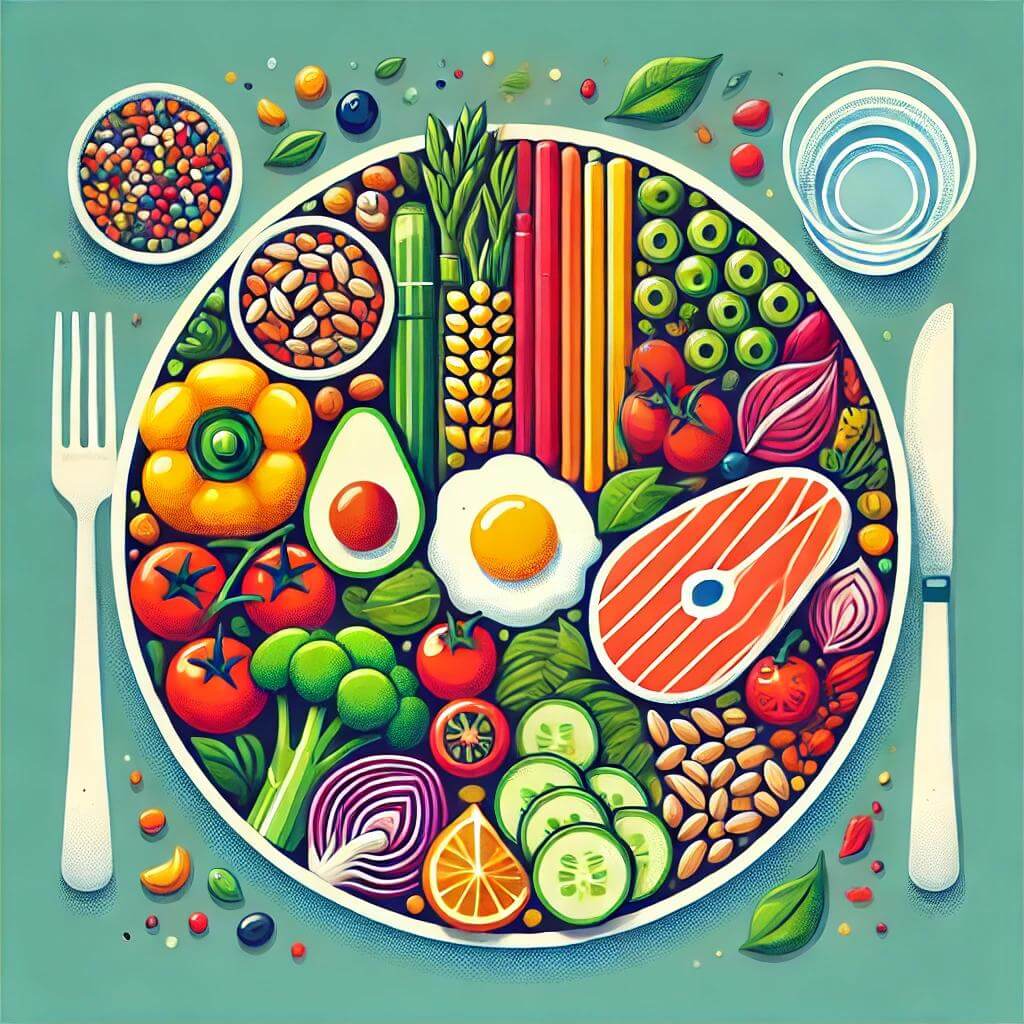
4. Balancing Your Plate
- Vegetables and Fruits: Aim to fill half your plate with vegetables and fruits at every meal. They are low in calories but high in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Proteins and Whole Grains: One-quarter of your plate should include lean proteins, and another quarter should be dedicated to whole grains or starchy vegetables.
- Healthy Fats: Add a small amount of healthy fat to your meals, such as a drizzle of olive oil or a handful of nuts.
5. Meal Timing and Frequency
- Regular Meals: Eating at consistent times each day helps regulate your metabolism and maintain energy levels.
- Snacking: Healthy snacks between meals can help prevent overeating and maintain blood sugar levels. Opt for snacks like yogurt, fruit, or a handful of nuts.
6. Portion Control
- Understanding Serving Sizes: Learning the appropriate portion sizes for different food groups is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet without overeating.
- Mindful Eating: Practice being present during meals, paying attention to hunger and fullness cues to avoid overindulgence.
7. Limiting Processed Foods
- Minimize Processed Food Intake: Processed foods are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium. Limit these foods to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Choose Whole Foods: Opt for whole, unprocessed foods as much as possible. Fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins should make up the bulk of your diet.
8. Incorporating a Variety of Foods
- Diverse Diet: Eating a wide variety of foods ensures you get a broad range of nutrients necessary for good health.
- Colorful Plates: Aim for a variety of colors on your plate, as different colors often represent different nutrients.
9. Reading Food Labels
- Nutritional Information: Understand how to read food labels to make informed choices about what you eat.
- Ingredient List: Be aware of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients that may be present in packaged foods.
10. Planning and Preparing Meals
- Meal Planning: Plan your meals ahead of time to ensure you have healthy options available and to prevent last-minute unhealthy choices.
- Batch Cooking: Preparing meals in advance can save time and reduce the temptation to eat unhealthy foods.
Benefits of a Healthy Nutrition Plan
1. Weight Management
- Calorie Control: A balanced diet helps you manage your weight by providing the necessary nutrients without excess calories.
- Satiety: Consuming a balanced diet with adequate protein and fiber helps you feel fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
2. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
- Heart Health: Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes Prevention: Managing carbohydrate intake and avoiding added sugars can help prevent or manage diabetes.
- Cancer Prevention: A diet high in antioxidants from fruits and vegetables can lower the risk of certain cancers.
3. Enhanced Mental Well-being
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals are essential for brain health and can improve mood and cognitive function.
- Stable Energy Levels: A balanced diet prevents the energy crashes that can contribute to mood swings and irritability.
4. Improved Digestive Health
- Fiber-Rich Foods: A diet high in fiber promotes regular bowel movements and prevents digestive disorders such as constipation and diverticulosis.
- Probiotics: Foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables support a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for digestion.
5. Stronger Immune System
- Nutrient-Dense Foods: Vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, and iron are vital for a strong immune system.
- Antioxidants: These help protect the body from oxidative stress and strengthen the immune system’s response to infections.
6. Sustainable Energy Levels
- Balanced Meals: Consuming a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats ensures steady energy levels throughout the day.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration supports physical performance and reduces fatigue.
7. Glowing Skin and Hair
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: Antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals from a balanced diet promote healthy skin and hair.
- Healthy Fats: Essential fatty acids keep skin hydrated and improve hair texture.
Practical Steps to Implement a Healthy Nutrition Plan
1. Start with a Plan
- Assess Your Current Diet: Take note of your current eating habits and identify areas for improvement.
- Set Realistic Goals: Determine what you want to achieve with your diet, whether it’s weight loss, improved energy, or better health.
2. Gradual Changes
- Small Adjustments: Begin by making small changes to your diet, such as swapping sugary snacks for fruits or incorporating more vegetables into meals.
- Consistency: Focus on being consistent with these small changes, which will lead to sustainable long-term habits.
3. Incorporate Physical Activity
- Exercise and Diet: A healthy diet goes hand-in-hand with regular physical activity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
- Balance: Choose activities you enjoy to make exercise a regular and enjoyable part of your routine.
4. Stay Motivated
- Track Progress: Keep a food diary or use an app to track your meals and monitor your progress.
- Reward Yourself: Set milestones and reward yourself with non-food-related treats when you reach your goals.
5. Seek Support
- Professional Help: Consult with a dietitian or nutritionist if you need personalized advice or have specific dietary needs.
- Community: Join a support group or find a diet buddy to help keep you accountable.
Summary Table
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Macronutrients | Balance carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in your diet for sustained energy and overall health |
| Micronutrients | Ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals through a varied diet |
| Hydration | Stay hydrated with water and other healthy fluids |
| Balanced Plate | Fill half your plate with vegetables and fruits, and the other half with proteins and grains |
| Meal Timing and Frequency | Eat regular meals and healthy snacks to maintain energy levels |
| Portion Control | Practice mindful eating and manage portion sizes to avoid overeating |
| Limiting Processed Foods | Minimize intake of processed foods and choose whole, unprocessed options |
| Incorporating Variety | Include a wide range of foods in your diet for a full spectrum of nutrients |
| Reading Food Labels | Learn to read food labels to make informed dietary choices |
| Planning and Preparing Meals | Plan and prepare meals in advance to ensure healthy options are always available |
Conclusion
Building a healthy nutrition plan is a journey that requires time, commitment, and patience. By focusing on the balance of macronutrients, incorporating a variety of micronutrient-rich foods, staying hydrated, and practicing portion control, you can create a sustainable and enjoyable eating pattern that supports long-term health. Remember, the key to a successful diet plan is consistency and making gradual changes that fit into your lifestyle.
*Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as health advice. The content is solely the personal opinion of the author and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or before starting any new diet or treatment. Read more



Post Comment